Fostering the debate through research and statistics
From its outset in the 1930s, the BIS has also served as a think tank for central banks. In its research and publications it focuses on policy issues of interest to monetary and financial authorities. The BIS also plays an important role in compiling and disseminating statistics on the international financial system, particularly those that shed light on issues related to financial stability.
1930 – 1945

BIS Economic Adviser Per Jacobsson and BIS Vice-President Leon Fraser at the World Economic and Monetary Conference, London, 1933.
1945 – 1961

The BIS Annual General Meeting, June 1955. The AGM is traditionally the occasion to present the Bank's Annual Economic Report.
1961 – 1979
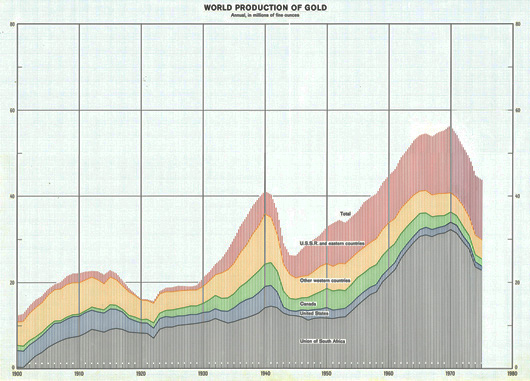
Gold played an important role in the Bretton Woods monetary system. Graph produced by the BIS Monetary and Economic Department charting the world production of gold between 1900 and 1975.
1980 – 2001

Per Jacobsson lecture in 1988 on The International Monetary System: the next Twenty-five Years. The BIS has a tradition of bringing together practitioners and researchers from both the private and public sectors.
2001 – 2020

