Financial stability implications of artificial intelligence - Executive Summary
The growing use of artificial intelligence (AI) by financial institutions is attracting closer regulatory scrutiny, including from a financial stability perspective. This expansion is driven by supply side factors, such as advances in large language models (LLMs), deep learning techniques, access to more unstructured data sources and increasing computational power, as well as demand side factors such as opportunities to reduce costs and the desire to stay competitive. Against this backdrop, the Financial Stability Board (FSB) report The Financial Stability Implications of Artificial Intelligence, published in November 2024, provides of stocktake of industry and regulatory/supervisory AI use cases and identifies potential implications for financial stability.
Drivers of AI use cases in the financial sector
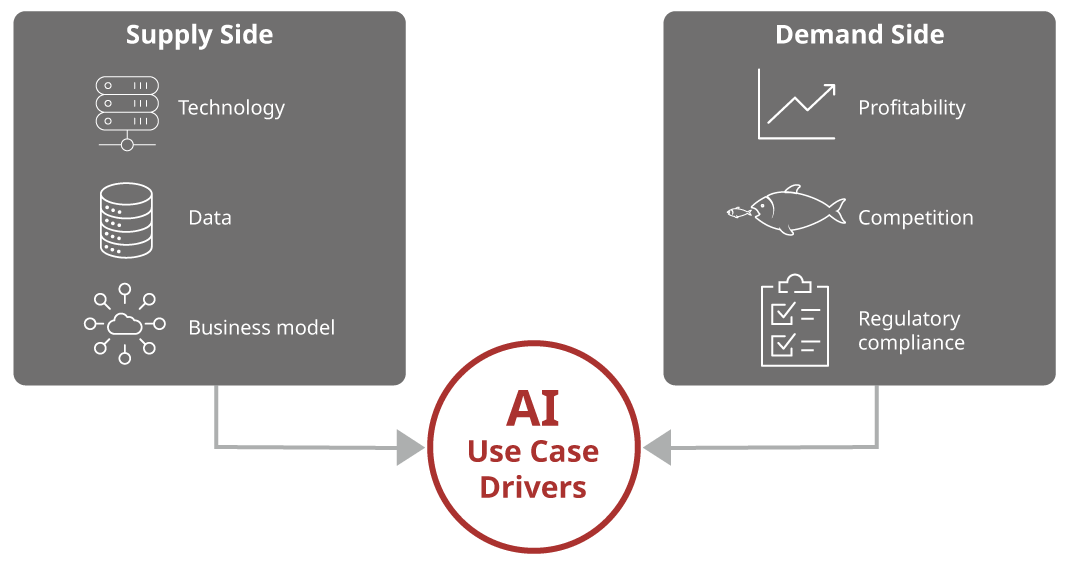
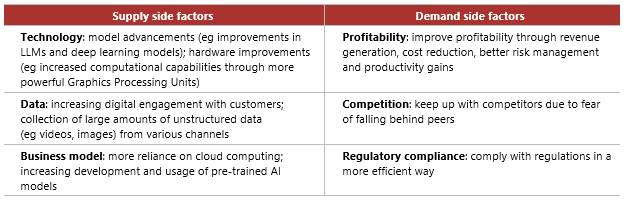
The report identified supply and demand side factors (summarised in the diagram and table below), noting that the former currently play a bigger role due to recent technological advancements.
AI use cases
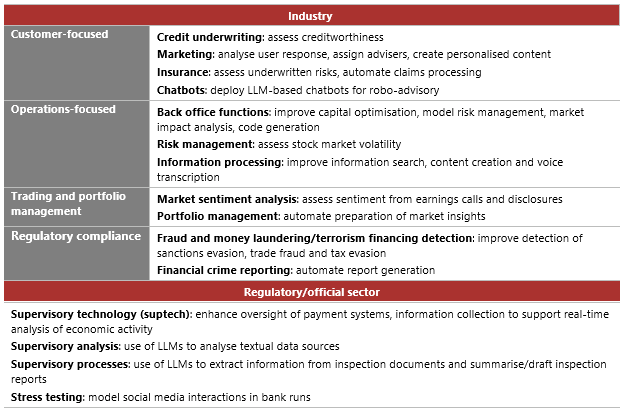
Financial institutions use AI mostly in enhancing internal operations and improving regulatory compliance. At present, use cases for revenue generation are limited, though firms are cautiously experimenting with generative AI (gen AI). The report adopts an activity-based framework to classify AI use cases, broken down by industry and regulatory/official sector, as follows:
Financial stability implications of AI
The use of AI in financial services without appropriate controls and oversight could amplify certain financial vulnerabilities, with potential implications for financial stability. The key AI-related developments that could have financial stability implications include:
- wider integration of AI in financial services, with increasing use in core business operations
- technological breakthroughs in LLMs and gen AI, enabling new applications but also introducing new risks
- growing reliance on specialised hardware and infrastructure services, concentrated among a few providers
- increasing use of unstructured and opaque training data sources, complicating data quality assessments and model validation
Financial authorities face two key challenges in evaluating the financial stability implications of AI that hinder effective vulnerability surveillance: significant uncertainty from rapid innovation and limited data on AI uptake. It is important to monitor potential financial stability implications that can arise from:
- Third-party dependencies and service provider concentration – eg reliance on a few dominant providers for AI hardware and cloud services
- Market correlations – eg widespread use of similar AI models and training data
- Cyber vulnerabilities – eg lower barriers for cyber criminals, enabling sophisticated attacks, such as model poisoning and disinformation campaigns
- Model risk, data quality and governance – eg lack of explainability of AI models and opaque training data, complicating validation and monitoring
- Other factors – eg gen AI facilitating fraud, such as deepfakes, synthetic identities and disinformation campaigns capable of triggering flash crashes or bank runs
Policy recommendations
The FSB recommends the following actions to address potential financial stability implications of the use of AI in the financial sector:
- Close data gaps – improve monitoring of AI adoption through periodic surveys, regulatory reporting, public disclosure and engagement with private sector stakeholders
- Review regulatory and supervisory frameworks – assess whether existing supervisory guidelines sufficiently address financial stability risks from AI use cases
- Enhance regulatory and supervisory capabilities – promote international cooperation and cross-sectoral sharing of information and good practices, and leverage AI tools to enhance regulatory and supervisory functions
