Fintech developments in the insurance industry - Executive Summary
Financial technologies or "fintech" innovations are reshaping the provision of financial services, creating new opportunities and posing new challenges for both the insurance industry and financial supervisors. In February 2017, the International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS) published the report FinTech Developments in the Insurance Industry, which describes fintech innovations that are relevant to the insurance industry and presents an overview of their potential impacts on the insurance sector and supervisory approaches.
Fintech innovations in insurance
Fintech innovations refer to the variety of emerging technologies and innovative business models that have the potential to transform the insurance business. In the insurance sector, the most relevant innovations are in terms of:
- Emerging technologies: digital platforms, the Internet of Things, telematics, big data, data analytics, comparators, robo advisors, machine learning, artificial intelligence and distributed ledger technology, including blockchain and smart contracts
- Business models: peer-to-peer, usage-based and on-demand insurance
Technological developments and the changing expectations of customers are the main drivers of innovation in the insurance industry. These innovations are being developed both by incumbent insurance companies and by new technology firms or new companies known as "insurtech" start-ups.
Potential impact of innovations in the insurance business
Fintech innovations have the potential to deliver a wide range of benefits - in particular, efficiency improvements, cost reductions, improved risk assessment, superior customer experience and greater financial inclusion. However, some of these innovations could also have negative implications for consumers and the financial stability of insurance markets.
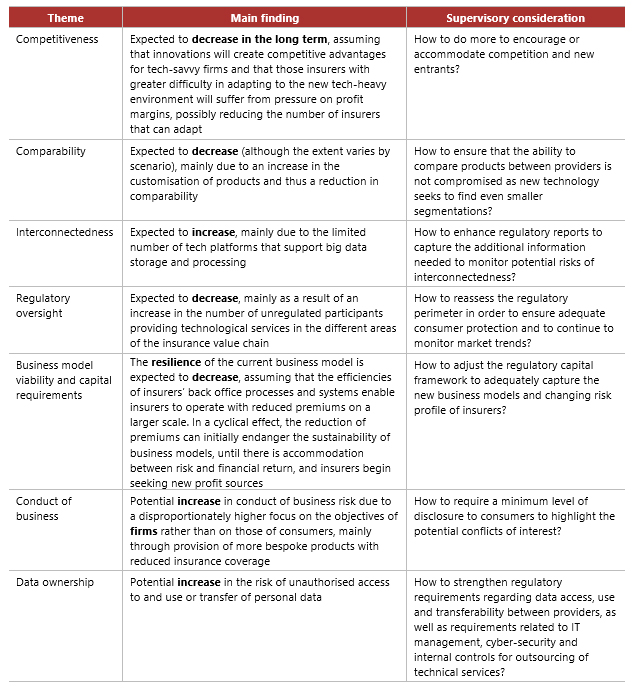
To identify the potential impact of these innovations, the IAIS considered the following three scenarios to assess the extent to which new technology firms could disrupt the insurance business model:
Scenario 1: Incumbent insurers successfully maintain their customer relationships and leverage technology firms to their own advantage.
Scenario 2: The insurance value chain becomes fragmented as new technology-enabled players enter the market. The traditional customer relationship weakens.
Scenario 3: Incumbent and traditional insurers are completely overtaken by "big tech" companies - such as Google, Amazon, Facebook or Apple - that provide insurance to fulfil emerging consumer needs.
The main findings from the scenario analysis are summarised below.
Challenges for insurance supervisors
Fintech developments are potentially disruptive and may have a significant impact on the insurance market. However, it is currently too uncertain an area to adequately assess and understand the extent to which these potential developments could affect the insurance market and its supervision.
Some of the other challenges that insurance supervisors may face in the near future in relation to fintech innovations are listed below:
- Supervisors need to understand how innovations work and are applied in order to adequately assess risks arising from new product and business models.
- Supervisors need to consider the risks of new innovations against the benefits for policyholders and the insurance sector as a whole and consider how to create a proper environment to foster innovation - for example, through regulatory sandboxes or innovation hubs - while safeguarding policyholders' interests.
- Supervisors and policymakers need to evaluate and, where appropriate, adjust their prudential regulation framework in order to capture new risks (such as the use of algorithms for underwriting purposes) and changes in corporate governance frameworks arising from third-party collaboration with insurtech companies.
- Supervisors need to consider whether current reporting requirements adequately allow the monitoring of trends and the potential build-up of risk arising from new technologies.
- Supervisors need to consider the impact of fintech innovations on consumer protection and the extent to which customers are treated fairly. For example, in the use of artificial intelligence and robo-advice technologies, safeguards should be in place to ensure that the advice and services provided are suitable and affordable for the customer.
- Supervisors need to establish cooperation and collaboration mechanisms with stakeholders, including supervised institutions and their associations, other market participants, academics, financial regulators and other authorities whose frameworks apply to fintech innovations, such as telecommunications or data protection agencies.
- Supervisors need to examine whether their supervisory tools and IT infrastructures need to be improved since technological innovation also offers opportunities for supervisors to automate certain supervisory processes and compliance requirements.
- Supervisory staff may need to acquire new technical skills to understand innovations and identify the associated risks. There is a need for supervisors to attract and retain talent with the relevant skillset.
* This Executive Summary and related tutorials are also available in FSI Connect, the online learning tool of the Bank for International Settlements.
